Ohm's Law Calculator
Calculate voltage, current, resistance, and power
Ohm's Law Calculator
Calculate voltage, current, resistance, and power using Ohm's Law
Ohm's Law
Ohm's Law is fundamental to electrical engineering, describing the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance.
Key Uses
• Circuit analysis and design
• Component sizing and selection
• Power calculations
• Safety considerations
About Ohm's Law
Ohm's Law describes the fundamental relationship between voltage, current, and resistance in electrical circuits.
It states that voltage equals current times resistance (V = I × R), forming the foundation of electrical engineering and circuit analysis.
This law was formulated by German physicist Georg Simon Ohm in 1827 and remains one of the most important principles in electronics.
Key Relationships
• V = I × R (Voltage = Current × Resistance)
• I = V / R (Current = Voltage / Resistance)
• R = V / I (Resistance = Voltage / Current)
• P = V × I (Power = Voltage × Current)
• P = I² × R (Power = Current² × Resistance)
• P = V² / R (Power = Voltage² / Resistance)
Ohm's Law Wheel
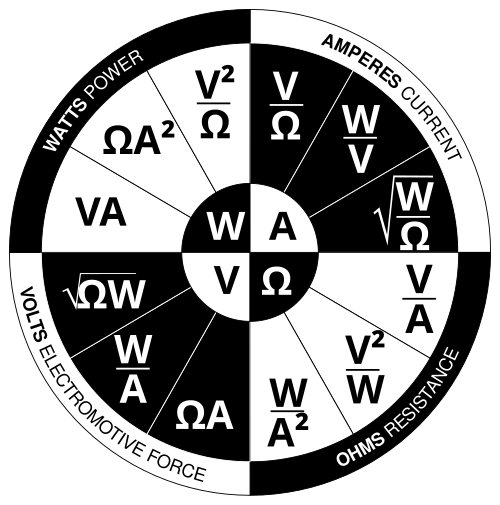
By Per Mejdal Rasmussen - Own work, inspired by Teaching Ohm's Law to Techs by Daniel Sullivan, CC BY-SA 3.0, Link
How to Use the Ohm's Law Wheel
The Ohm's Law wheel is a visual reference tool that helps you quickly find the right formula for any electrical calculation.
To use it: Cover the unknown quantity (V, I, R, or P) with your finger or thumb, and the remaining visible formulas will show you how to calculate it.
For example, if you want to find voltage (V), cover the V in the center, and you'll see the formulas I×R, √(P×R), and P/I around it.
💡 Tip: This wheel includes all 12 possible formulas for calculating voltage, current, resistance, and power using Ohm's Law and the power equations.
Ohm's Law Wheel image: Wikipedia - Ohm's Law
Common Applications & Use Cases
Circuit Design
- • LED current limiting resistors
- • Voltage divider circuits
- • Component selection
- • Load calculations
Power Analysis
- • Power consumption calculations
- • Heat dissipation analysis
- • Battery life estimation
- • Efficiency measurements
Safety & Troubleshooting
- • Component ratings verification
- • Fault diagnosis
- • Safety calculations
- • Performance optimization
Practical Examples
Example 1: LED Circuit
Problem: Calculate the resistor needed for a 3.3V LED with 20mA current from a 5V supply.
Solution:
• Voltage across resistor: 5V - 3.3V = 1.7V
• Using R = V / I: R = 1.7V / 0.02A = 85Ω
• Use standard 100Ω resistor (closest higher value)
Example 2: Power Calculation
Problem: Find the power dissipated by a 1kΩ resistor with 12V across it.
Solution:
• Using P = V² / R: P = (12V)² / 1000Ω
• P = 144 / 1000 = 0.144W = 144mW
• A 1/4W (250mW) resistor would be adequate